Understanding Base64 Encoding
Michelle RobertsShare
Base64 encoding plays a crucial role in SSL Certificate management and secure data transmission across the internet.
This encoding method transforms binary data into a format that can be safely transmitted through systems that only handle ASCII text, making it essential for e-mail attachments, SSL Certificate signing requests (CSRs), and various security implementations.
Understanding Base64 Encoding
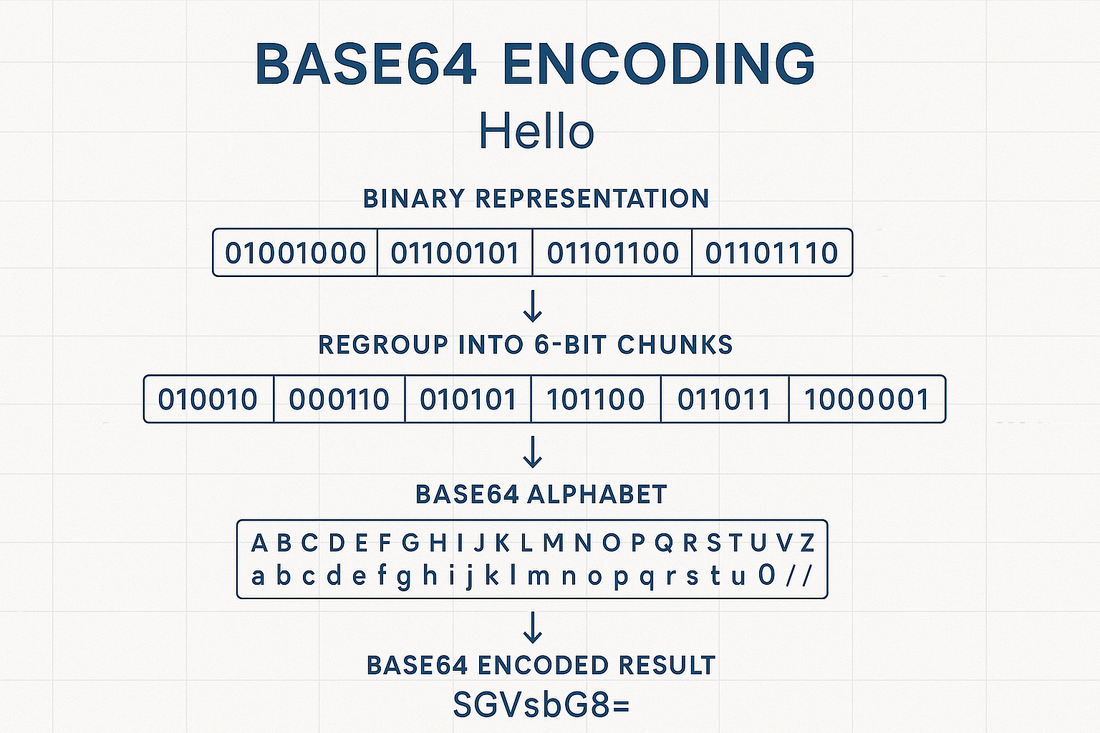
Base64 is an encoding scheme that converts binary data into a set of 64 different ASCII characters.
These characters include uppercase letters A-Z, lowercase letters a-z, numbers 0-9, and two additional characters (typically + and /).
This encoding ensures that sensitive data, including SSL Certificate information, can be transmitted reliably across different platforms and systems without corruption.
The Technical Foundation of Base64
The encoding process works by taking three bytes of binary data (24 bits) and converting them into four Base64 characters (6 bits each).
When the input data length is not divisible by three, padding characters (=) are added to maintain proper alignment.
This mathematical precision ensures that SSL Certificate requests and other security-related data maintain their integrity during transmission.
Common Applications in SSL Certificate Security
Base64 encoding is fundamental to many aspects of SSL Certificate management. Certificate Signing Requests (CSRs), private keys, and the SSL Certificates themselves are typically encoded in Base64 format within the PEM (Privacy Enhanced Mail) container.
This standardization ensures compatibility across different server platforms and security systems.
Base64 in SSL Certificate Management
When working with Trustico® SSL Certificates, administrators frequently encounter Base64 encoded data.
The CSR generation process outputs Base64 encoded text, which must be submitted to the Certificate Authority (CA) for SSL Certificate issuance.
Similarly, the issued SSL Certificates arrive in Base64 format, making it crucial to understand this encoding method for proper SSL Certificate installation and management.
Security Implications
While Base64 encoding provides a reliable way to transmit binary data, it is important to note that it is not an encryption method.
The encoding can be easily reversed, which is why additional security measures, such as SSL Certificate encryption and secure transmission protocols, are essential when handling sensitive information.
Practical Applications and Usage
System administrators and developers regularly work with Base64 encoding when managing SSL Certificates.
The encoded format appears in various configuration files, including Apache and Nginx web server configurations.
Understanding how to recognize and handle Base64 encoded data is essential for proper SSL Certificate installation and troubleshooting.
E-Mail Security and Base64
In e-mail systems, Base64 encoding ensures that SSL Certificate-related communications and attachments remain intact during transmission.
This is particularly important when receiving SSL Certificates from Trustico® or when exchanging security-related information with technical support teams.
Troubleshooting Base64 Issues
Common challenges with Base64 encoded SSL Certificates often relate to line breaks, character corruption, or incomplete copying.
When installing SSL Certificates, ensuring the Base64 encoded data remains exactly as provided is crucial for proper functionality. Extra spaces, line breaks, or missing characters can cause installation failures or security warnings.
Best Practices for Handling Base64 Data
When working with Base64 encoded SSL Certificates, maintaining data integrity is paramount.
Always use proper text editors that do not modify line endings or character encoding.
Keep backup copies of original SSL Certificates and verify the format matches the expected Base64 pattern before installation or submission.
Future Developments and Standards
As internet security continues to evolve, Base64 remains a fundamental component of SSL Certificate management and secure communications.
Modern security protocols and SSL Certificate standards still rely on this encoding method, making it an essential concept for anyone involved in web security and SSL Certificate administration.
Conclusion
Base64 encoding serves as a crucial bridge between binary data and text-based systems, particularly in the context of SSL Certificates and secure communications.
Understanding its role and proper implementation helps ensure successful SSL Certificate deployment and management.
For organizations seeking to maintain robust security infrastructure, working with trusted providers like Trustico® ensures proper handling of Base64 encoded SSL Certificates and related security components.



